Types of Atomic Radius
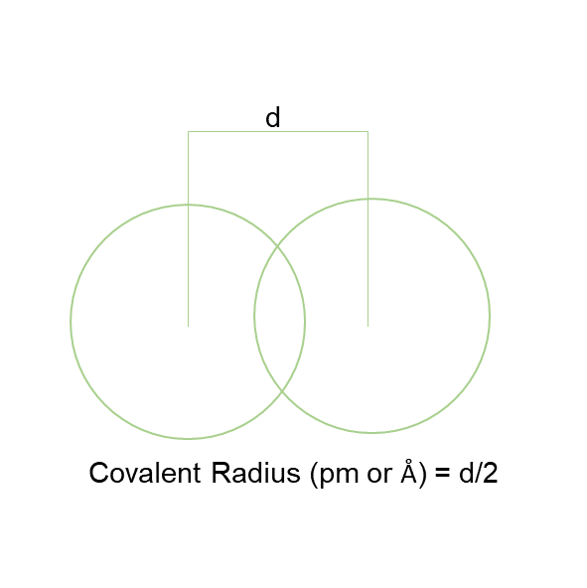
Covalent Radius [1]
Covalent radius is half of the internuclear distance between the two covalently bonded atoms of the same element in a molecule.
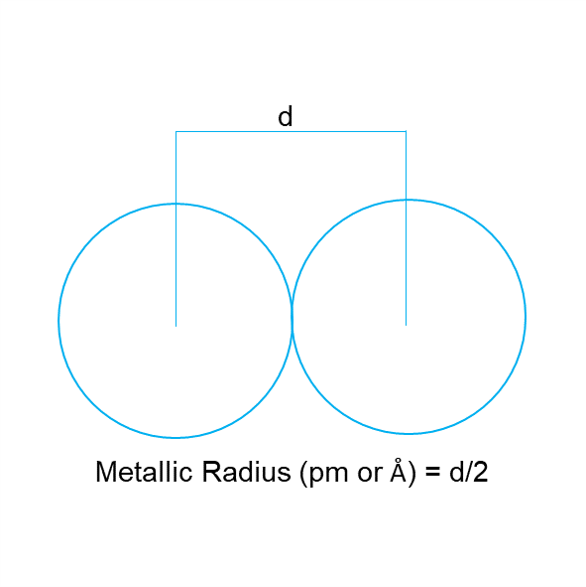
Metallic Radius [2]
The metallic radius is half the internuclear distance between the two atoms of the metal held together by a metallic bond.
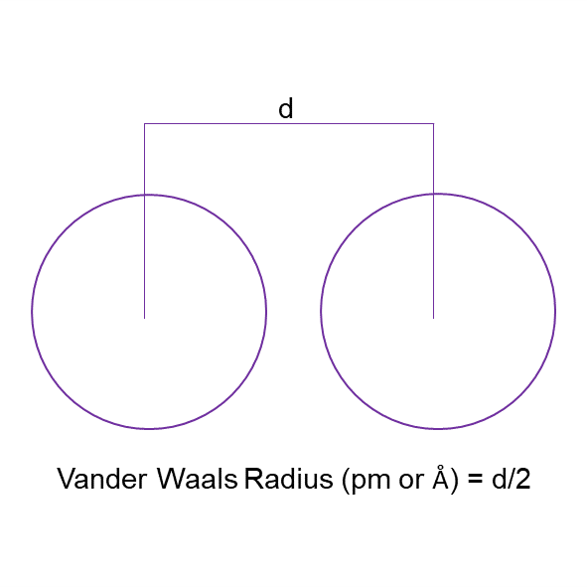
Vander Waal Radius [3]
The Vander Waal radius is half the distance between the center of the nuclei of the two nonbonded atoms.
Note: Since the internuclear distance is the smallest for covalent radius and
highest for Vander
Waal radius, therefore the increasing order of atomic radius is:
Covalent radius < Metallic radius < Vander Waal Radius
1. Beatriz Cordero, Verónica Gómez, Ana E Platero-Prats, Marc Revés, Jorge Echeverría, Eduard Cremades, Flavia Barragán, and Santiago Alvarez. Covalent radii revisited. Dalton Transactions, pages 2832, 2008.
2. William M Haynes. CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics. 100 Key Points. CRC Press, London, 95th edition, 2014. ISBN 9781482208689.
3. Kyle & laby tables of physical & chemical constants. (2017). 3.7.5 atomic radii. [Online; accessed 30-April-2017].
Covalent radius < Metallic radius < Vander Waal Radius
References
The references for the values of the atomic radius taken for the analysis is given below:1. Beatriz Cordero, Verónica Gómez, Ana E Platero-Prats, Marc Revés, Jorge Echeverría, Eduard Cremades, Flavia Barragán, and Santiago Alvarez. Covalent radii revisited. Dalton Transactions, pages 2832, 2008.
2. William M Haynes. CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics. 100 Key Points. CRC Press, London, 95th edition, 2014. ISBN 9781482208689.
3. Kyle & laby tables of physical & chemical constants. (2017). 3.7.5 atomic radii. [Online; accessed 30-April-2017].